Reconciliation loop
Modules
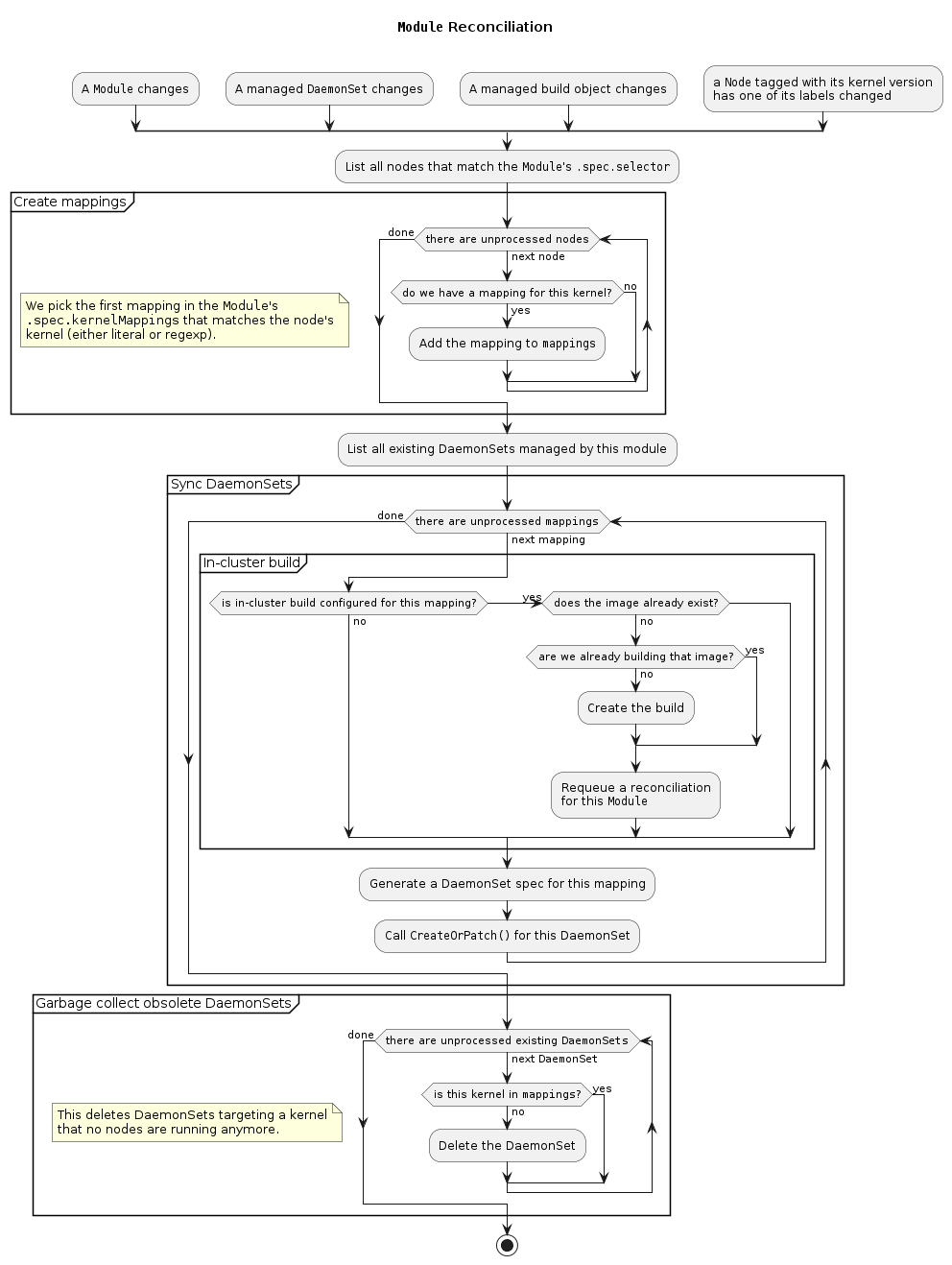
Each time a new Module is created, we need to find to which nodes it applies.
-
A first filtering is performed using the
.spec.selectorfield, then we go through the module’s kernel mappings to find a container image that matches the node’s kernel. -
We end up with a certain number of (kernel, image) pairs; for each of these pairs, there should be a
DaemonSet. -
We first look for a
DaemonSetthat would already be targeting the same kernel and DriverContainer image (that data is stored in theDaemonSet’s labels). -
If there is already such a
DaemonSet, we patch it, if needed. -
If there is not already a matching
DaemonSet, we create it and set theModuleas owner. -
When a
Moduleis deleted, we have nothing to do: because we set it as owner of allDaemonSets, Kubernetes garbage collection will take care of deleting them. -
We watch
Module, ownedDaemonSetand build objects as well as nodes to make sure that we are not missing any change in the cluster.